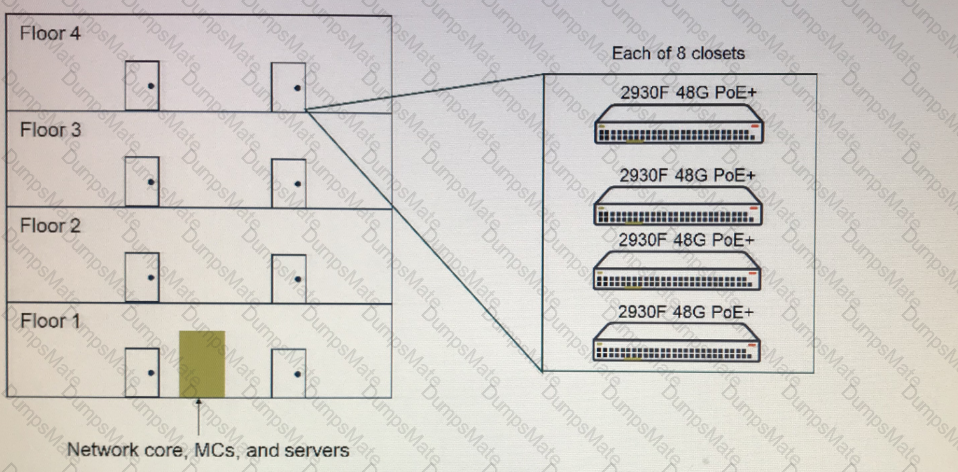
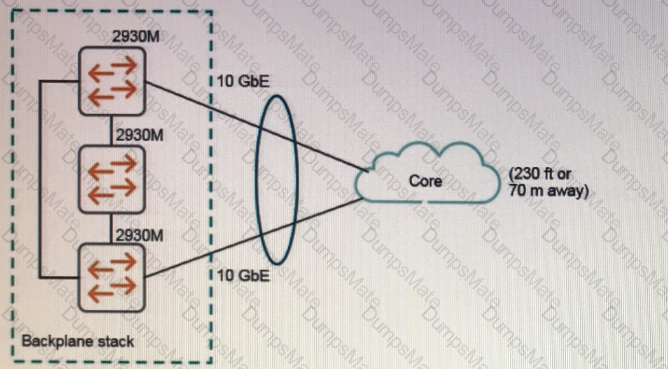
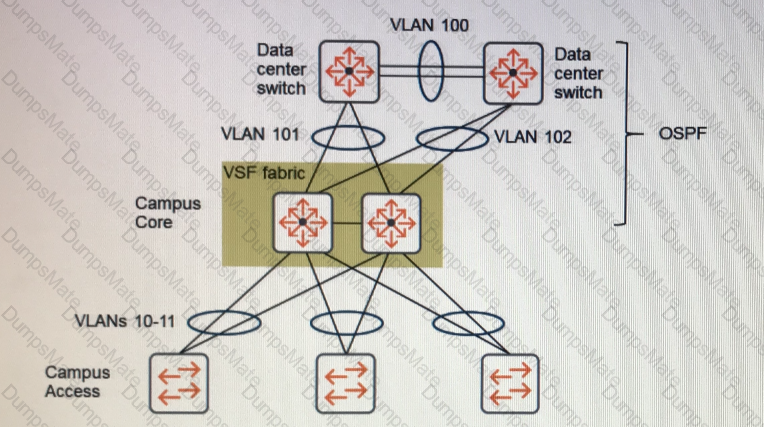
Explanation: The Aruba SDN Controller is a software component that runs on the Mobility Master (MM) and provides centralized control and management of the network devices and applications that support the SDN services. The SDN Controller communicates with the network devices through the southbound interface (SBI) and exposes the northbound API (NBAPI) for the SDN applications to access the network resources and services1.
One of the SDN applications that can integrate with the Aruba SDN Controller is the Aruba UC and Collaboration Solution, which optimizes the performance and quality of Skype for Business traffic over the wireless network. The Aruba UC and Collaboration Solution consists of three components: the Aruba UC and Collaboration SDN Application, the Aruba UC and Collaboration Dashboard, and the Aruba UC and Collaboration Agent2.
The Aruba UC and Collaboration SDN Application is a software module that runs on the Skype for Business Front End Server and communicates with the Aruba SDN Controller through the NBAPI. The Aruba UC and Collaboration SDN Application monitors the Skype for Business sessions and events, and sends the relevant information to the Aruba SDN Controller, such as the user identity, device type, session type, codec, bandwidth, and quality of service (QoS) requirements2.
The Aruba UC and Collaboration Dashboard is a web-based graphical user interface that provides visibility and analytics of the Skype for Business sessions and events over the wireless network. The Aruba UC and Collaboration Dashboard connects to the Aruba SDN Controller through the NBAPI and displays the information collected by the Aruba UC and Collaboration SDN Application, such as the number of active sessions, session types, session quality, bandwidth consumption, and device distribution2.
The Aruba UC and Collaboration Agent is a software module that runs on the Mobility Controller (MC) and communicates with the Aruba SDN Controller through the SBI. The Aruba UC and Collaboration Agent receives the information from the Aruba UC and Collaboration SDN Application through the Aruba SDN Controller, and applies the appropriate QoS policies and actions on the wireless network, such as prioritizing the Skype for Business traffic, marking the DSCP values, reserving the bandwidth, and adjusting the airtime2.
To support high availability for the SDN services, the Aruba SDN Controller must be deployed in a redundant configuration, with a primary MM and a backup MM. The primary MM runs the active instance of the Aruba SDN Controller, while the backup MM runs the standby instance of the Aruba SDN Controller. The backup MM synchronizes the configuration and state information from the primary MM, and takes over the SDN Controller role in case of a failure or switchover of the primary MM1.
The other options do not provide high availability specifically for the SDN services, although they may provide redundancy for other aspects of the wireless network. A redundant master MC does not run the Aruba SDN Controller, and only provides backup for the master MC role, which is responsible for managing the configuration and licensing of the MCs in the network3. Backup controllers defined on the APs do not run the Aruba SDN Controller, and only provide backup for the local MC role, which is responsible for terminating and managing the APs in the network4. A cluster deployment for MCs does not run the Aruba SDN Controller, and only provides load balancing and fast failover for the APs in the network5.
References: 1: ArubaOS 8.7 User Guide - Aruba, Chapter 42: SDN Controller, pages 1049-1050. 2: Aruba UC and Collaboration Solution Guide - Aruba, Chapter 2: Aruba UC and Collaboration Solution Overview, pages 11-15. 3: ArubaOS 8.7 User Guide - Aruba, Chapter 2: ArubaOS Architecture, pages 25-26. 4: ArubaOS 8.7 User Guide - Aruba, Chapter 3: Configuring Controller Redundancy, pages 39-40. 5: ArubaOS 8.7 User Guide - Aruba, Chapter 4: Configuring Controller Clustering, pages 51-52.